A PFD is a compulsory piece of equipment that is found onboard all vessels.
Taking safety precautions when out on the water is crucial.
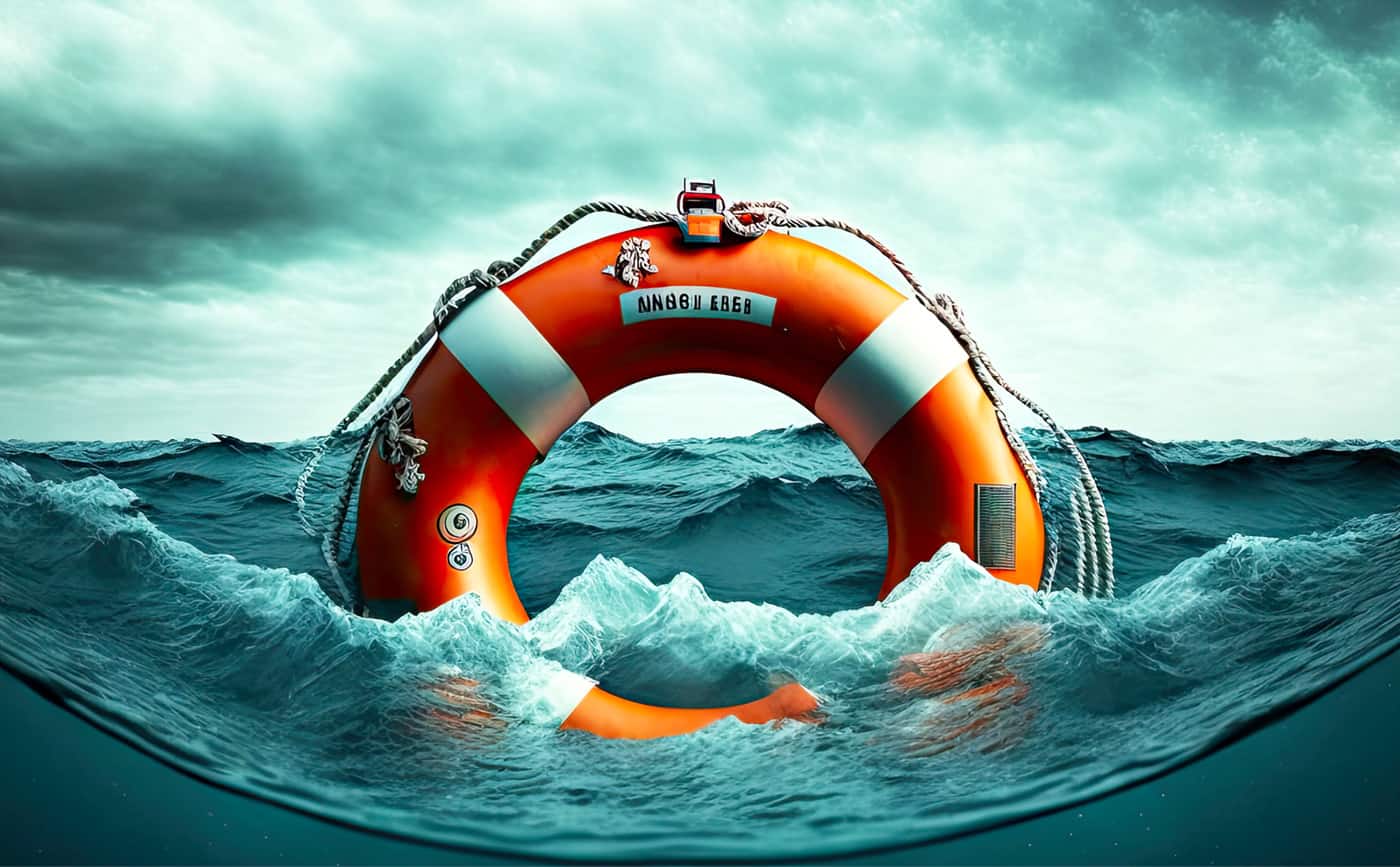
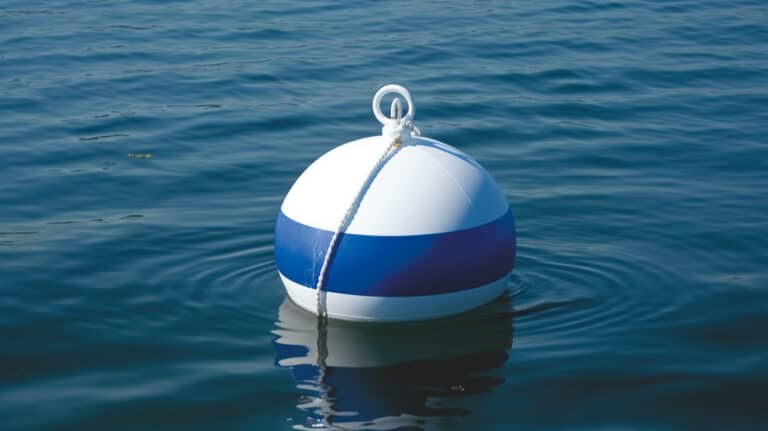
A Type IV PFD is a personal floatation device that is intended to be thrown into the water rather than worn by the individual who is in trouble.
An example of a type IV PFD is a life ring, a buoyant cushion, or a horseshoe buoy that has around 16.5 pounds of buoyancy.
Due to the design of this type of PFD, it should not be cast out to those who will be unable to grasp onto it, or used in rough waters.
This type of PFD differs from many other types as it is intended to be thrown and held onto, rather than worn.
As with most types of PFDs, there are several advantages associated with the use of an IV PFD.
The main advantage is that it has a universal design because a Type IV PFD is thrown out to the individual who has got into trouble in the water.
All passengers who are on the boat should already be wearing a life jacket so a Type IV PFD is cast into the water to provide them with additional support.
This concept also means that it can be used by any individual regardless of their size and shape.
Once it has reached the individual, they can then hold onto it.
As mentioned, all passengers on board should be wearing a life jacket regardless of their age, so a type IV PFD should not be used as a substitute for a life jacket (learn how to properly store PFDs).
If a passenger falls overboard, their life jacket will provide them with the initial support, and the Type IV PFD will be used to provide further aid.
Though the lack of size restrictions is deemed to be one of the most prominent advantages of using a Type IV PFD, there are many others to be aware of.
We have identified these below.
Easy To Use – when you are faced with an emergency, you must act fast.
Luckily a Type IV PFD allows you to do this.
Most other types of emergency equipment need to be worn before they are activated and helpful in any way.
This type of PFD however does not, instead, it just needs to be thrown into the water in the direction of the individual who requires help.
Location Marker – often a Type IV PFD will be cast into the water to mark the location where the individual fell overboard.
Once in the water, it will remain in or near the location where the victim was last seen.
This then enables the boat operator to establish a rescue search as they have a better idea of the area where the victim went missing.
Although this is a useful aid, it may not be as dependable in rougher waters where there is a risk of the PFD moving around.
It can be towed – these PFDs are typically designed with an attachment feature that will allow you to tie a rope to it.
When thrown into water the rope will then remain secured to the Type IV PFD and the other end can be held by someone who is still on the boat.
This then makes it easier to tow the victim back towards the boat and out of the water.
Whilst this is of course beneficial to the individual who is stranded in the water, it also means that other people who are on board aren’t required to jump into the water and swim towards the victim to get them back to safety, instead, the rope can be used to pull them.
Aren’t bulkily designed – in comparison to most other types of PFDs, a Type IV PFD does not boast a bulky design and typically tends to have a lightweight feel.
Wearable PFDs can often feel a little weighty, requiring the wearer to apply more effort to the tasks of keeping themselves afloat.
However, this type of PFD will not subject the victim to the same issues, instead, they have the flexibility to grab it comfortably and aren’t held down by something that is overly bulky.
What Are The Approved Type IV PFDs?
Three different types of IV PFDs are approved for use in the water and some are more commonly found on boats than others.
Ring Buoys
A ring buoy is perhaps the most common type IV PFD that is typically found on harbors and onboard the decks of boats.
They are donut-shaped and brightly colored to ensure that they stand out on the surface of the water.
Victims have the choice of holding onto the buoy or putting it over their heads and arms.
Many ring buoys are now designed with lights that can be activated before throwing them into the water.
As such, this makes it much easier to rescue victims at night and during poor visibility.
Buoyant Cushion
Buoyant cushions are typically square-shaped and as expected, resemble the look of a cushion.
These cushions are designed with straps in which the victim can put their arms through if they require extra assurance that it isn’t going to move along with better stability.
They typically have a large surface area that provides the victim with plenty of space to lie as they wait to be rescued.
Alternatively, some may choose to position it under their chest and then begin swimming back towards the boat.
Horseshoe Buoys
As implied by its title, a horseshoe buoy is shaped like a horseshoe.
They are typically designed with a plastic core and vinyl coating.
Like most other type IV PFDs, they are brightly colored (typically bright yellow) to ensure that they stand out once they have been thrown into the water.
Most have a canister that attaches to the victim via a lanyard.
Final Thoughts
There are many advantages associated with the use of a Type IV PFD, however, in no situation should the use of this type of device be substituted for a life jacket (the best are listed here).
All passengers onboard a vessel should be wearing a life jacket and this device should then be used to provide additional support.